Mountains, canyons, plains — these geological features are not only present on land, but also under the sea, where scientists have now charted them in incredible detail in the ocean surrounding Antarctica. The five-year project mapped 18.5 million square miles, and even revealed a new deepest point in the Southern Ocean, a depression lying 7,432 meters (24,383 feet) below sea level called the Factorian Deep. This study and others like it around the world are filling major scientific gaps in our understanding of what the ocean floor looks like, a key part of knowing how to foster ocean health. More mapping also enables us to make an even stronger science-backed case for marine protected areas. If you want to turn this positive progress into action, you can join us today as we call on world leaders to protect Antarctica and secure the largest act of ocean protection in history. We’re close to reaching our goal of 250,000 petition signatures!
Call on France to strengthen its marine protected areas.
Following the international agreement at the Convention on Biological Diversity (COP 15), 190 countries committed to protecting 30% of the ocean by 2030, sparking new hope for the ocean.
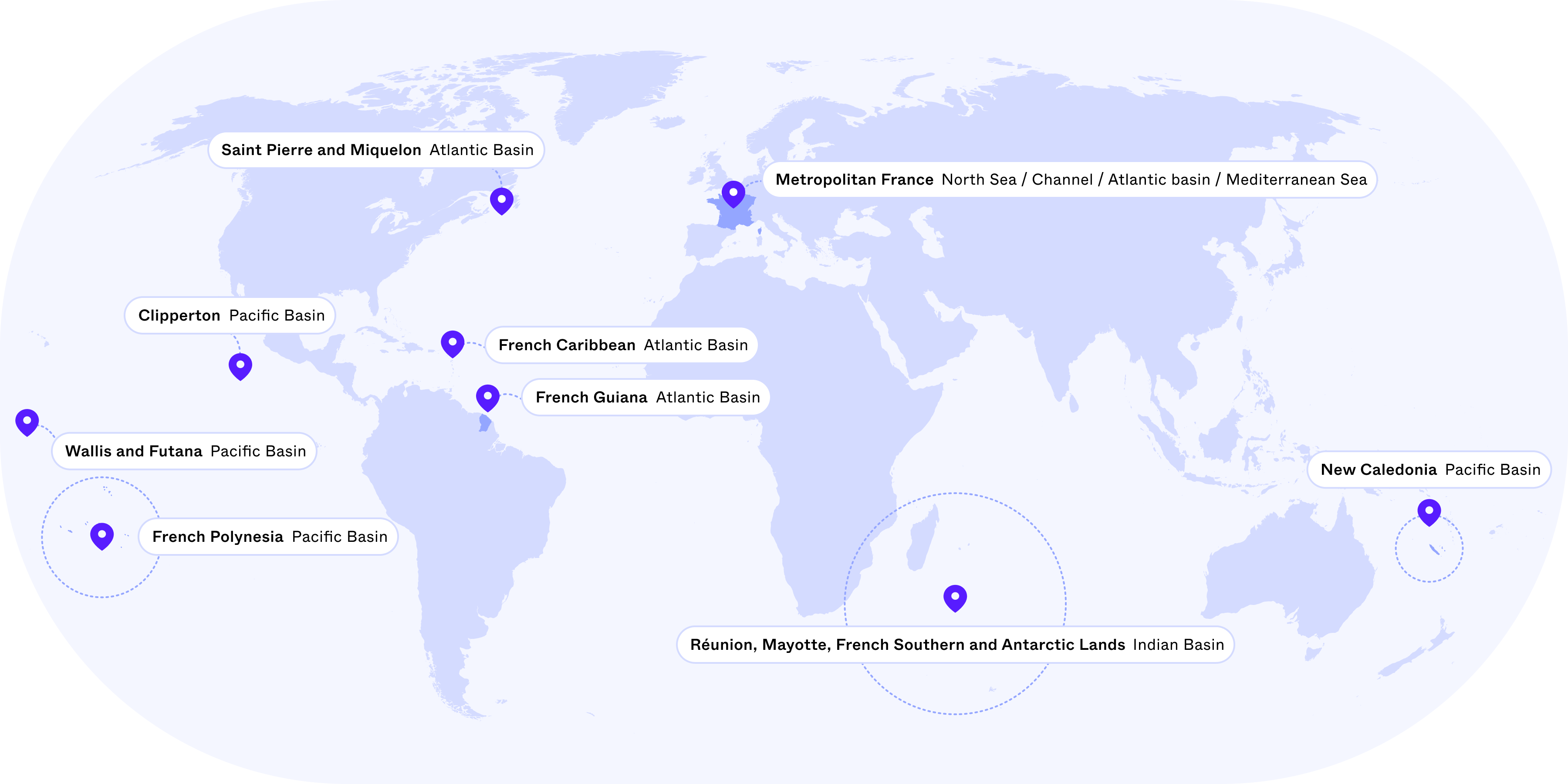
While France claims to be a champion of climate and biodiversity on the international stage, the current conservation policy implemented in its maritime territories is far from adequate, and undermines its international posture.
Given that France oversees the world’s second-largest maritime territory (nearly 11 million square kilometers), it has a critical responsibility to promote the health of the ocean — a crucial regulator of the climate and the largest living space on the planet.